一、Python堆heapq
什么是堆:堆是二叉树,最大堆中父节点大于或等于两个子节点,最小堆父节点小于或等于两个子节点。( heapq库中的堆默认是最小堆)
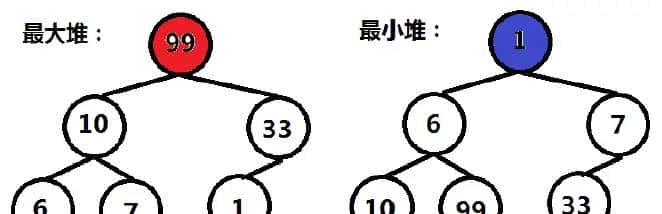
python 中的heapq模块提供了堆排序算法的实现,具体用法如下:
-
创建堆:只有最小堆,没有最大堆,想要有最大堆的效果,可以将数据取相反数
-
- heapq.heappush
heapq.heappush(heap, item) 将item压入到堆数组heap中并自动生成最小堆。
如果不进行此步操作,后面的heappop()失效,会直接返回原列表第一个值,而且必须从头开始heappush,不然也会返回原列表第一个值。
- heapq.heappush
-
- heapq.heapify
heapq.heapify(list)参数必须是list,此函数将list变成堆,实时操作。从而能够在任何情况下使用堆的函数
- heapq.heapify
-
访问堆内容
-
- heapq.heappop
heapq.heappop(heap)弹出最小值,由于堆的特征是heap[0]永远是最小的元素,所以一般都是删除第一个元素。
注意,如果不是压入堆中,而是通过append追加一个数值,堆的函数并不能操作这个增加的数值,或者说它堆对来讲是不存在的。
- heapq.heappop
-
- heapq.heappushpop
heapq.heappushpop(heap, item)是上述heappush和heappop的合体,同时完成两者的功能,注意:相当于先操作了heappush(heap,item),然后操作heappop(heap)
- heapq.heappushpop
-
- heapq.nlargest
heapq.nlargest(n, iterable,[ key])查询堆中的最大n个元素
- heapq.nlargest
-
- heapq.nsmallest
heapq.nsmallest(n, iterable,[ key])查询堆中的最小n个元素
- heapq.nsmallest
-
更新/替换堆
-
- heapq.heaprepalce
heapq.heapreplace(heap, item)是上述heappop和heappush的联合操作。注意:与heappushpop(heap,item)的区别在于,顺序不同,这里是先进行删除,后压入堆
- heapq.heaprepalce
1. heapq.heappush & heapq.heappop
import heapq
nums = [21, 13, 52, 16, 34, 21, 119]
heap = []
for num in nums:
heapq.heappush(heap, num)
print(heap[0]) # 弹出最小值,使用heap[0]
print([heapq.heappop(heap) for _ in range(len(nums))]) # 堆排序结果
结果:
13
[13, 16, 21, 21, 34, 52, 119]
2. heapq.heapify
import heapq
nums = [21, 13, 52, 16, 34, 21, 119]
heapq.heapify(nums)
print(nums[0]) # 弹出最小值,使用nums[0]
print([heapq.heappop(nums) for _ in range(len(nums))]) # 堆排序结果
结果:
13
[13, 16, 21, 21, 34, 52, 119]
3. heapq.heappop & heapq.nlargest & heapq.nsmallest
# heapq.heappop 参考上述代码
import heapq
nums = [21, 13, 52, 16, 34, 21, 119]
print(heapq.nlargest(3, nums))
print(heapq.nsmallest(3, nums))
结果:
[119, 52, 34]
[13, 16, 21]
# 这两个函数还接受一个参数key,用于处理dict等类型数据
score= [
{ name : xiaoming , score : 100},
{ name : xiaozhang , score : 90},
{ name : xiaoli , score : 92},
{ name : xiaowang , score : 65},
{ name : xiaosun , score : 78}
]
print(heapq.nsmallest(3, score, key=lambda s: s[ score ]))
print(heapq.nlargest(3, score, key=lambda s: s[ score ]))
结果:
[{ score : 65, name : xiaowang }, { score : 78, name : xiaosun }, { score : 90, name : xiaozhang }]
[{ score : 100, name : xiaoming }, { score : 92, name : xiaoli }, { score : 90, name : xiaozhang }]
4. heapq.heaprepalce
import heapq
nums = [21, 13, 52, 16, 34, 21, 119]
heapq.heapify(nums)
heapq.heapreplace(nums, 23)
print([heapq.heappop(nums) for _ in range(len(nums))])
结果:
[16, 21, 21, 23, 34, 52, 119]
二、堆排序
方法一
import heapq
def heapsort(nums):
h = []
for value in nums:
heapq.heappush(h,value)
return [heapq.heappop(h) for _ in range(len(h))]
print(heapsort([1,3,5,7,9,2,4,6,8,0]))
方法二
import heapq
def heapsort(nums):
heapq.heapify(nums)
return [heapq.heappop(nums) for _ in range(len(nums))]
print(heapsort([1,3,5,7,9,2,4,6,8,0]))
方法一和二无本质区别,只是构建堆的方式不一样。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。如内容涉嫌侵权,请在本页底部进入<联系我们>进行举报投诉!
THE END




















暂无评论内容