DeepSeek-V3.2 Agent 开发入门
本篇将依次从 DeepSeek-V3.2 模型简介、快速上手使用方法以及与 LangChain 集成三个方面展开介绍,并包含可运行示例供大家学习实验。
一、DeepSeek-V3.2 简介
DeepSeek-V3.2 通过引入可拓展的 GRPO 训练框架搭配大规模合成 Agent 任务数据集,借助海量强化学习后训练,让模型一举突破性能极限。在数学、编程、Agent 性能方面全面领先,整体追平全球性能最强劲模型 Gemini 3.0 Pro。
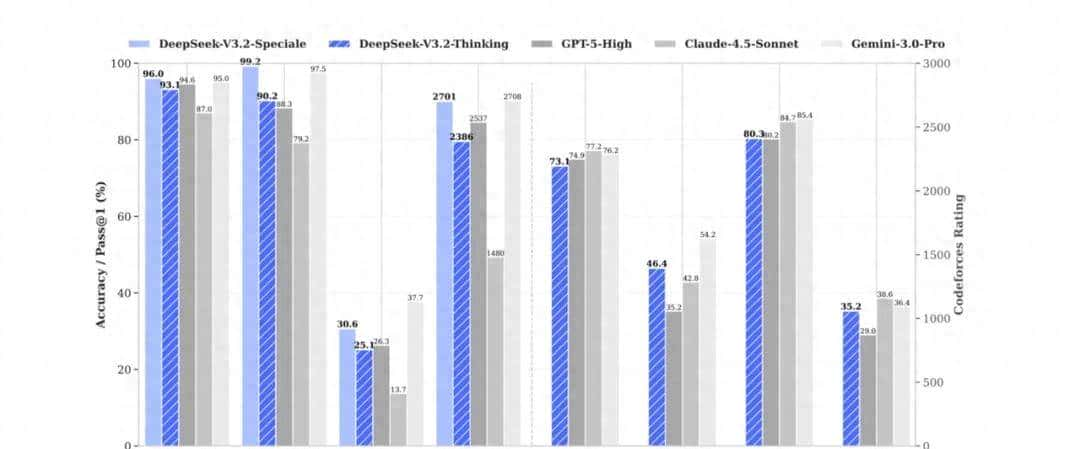
DeepSeek-V3.2 模型价格极具竞争力:
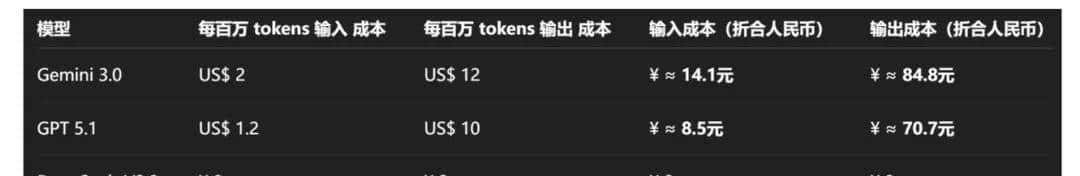
DeepSeek-V3.2 模型的 API 已全面上线,模型权重也已全面开源。
- 模型权重:https://huggingface.co/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.2
- 模型详解文章:DeepSeek V3.2重磅发布:性能比肩gemini 3.0 Pro,价格不足五分之一!打破垄断,开源界注入强心剂!
- LangChain 1.0 入门教程:LangChain 1.0 入门实战教学
二、DeepSeek V3.2 快速上手使用
- 基础配置
第一注册 DeepSeek 账号并获取 API Key( https://platform.deepseek.com/usage )。
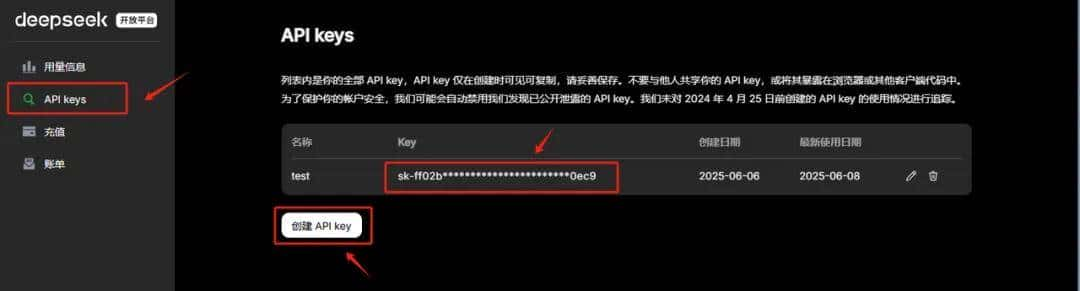
在项目根目录创建 .env 文件存储 API Key:
2. 基础调用示例
加入 赋范大模型技术社区:https://brmes.xet.tech/s/4mjiyo 免费领取 完整项目代码及示例,还有更多Agent 开发实战内容等你来拿

"""
DeepSeek API 基础调用示例
该脚本展示了如何配置环境并调用 DeepSeek 对话接口。
"""
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from openai import OpenAI
# 加载环境变量
load_dotenv(override=True)
DeepSeek_API_KEY = os.getenv("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY")
def basic_chat_demo():
"""
演示基础对话功能
"""
# 初始化 DeepSeek 的 API 客户端
# 参数注释:
# api_key: 从环境变量获取的 DeepSeek API 密钥
# base_url: DeepSeek 官方 API 地址
client = OpenAI(api_key=DeepSeek_API_KEY, base_url="https://api.deepseek.com")
# 调用 DeepSeek 的 API,生成回答
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "你是乐于助人的助手,请根据用户的问题给出回答"},
{"role": "user", "content": "你好,请你介绍一下你自己。"},
],
)
# 打印模型最终的响应结果
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
if __name__ == "__main__":
basic_chat_demo()三、DeepSeek-V3.2 Function Calling 调用流程
Function Calling 是大模型调用外部工具的关键技术。
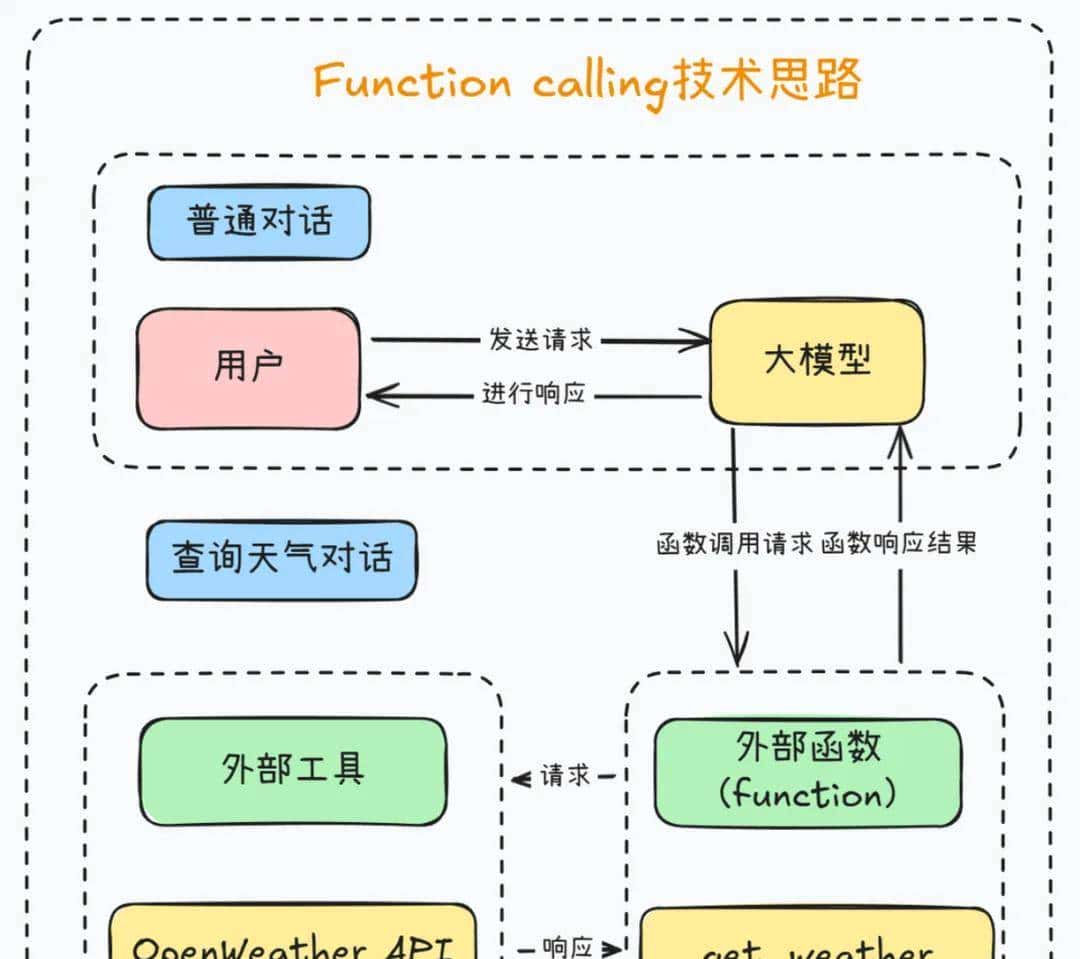
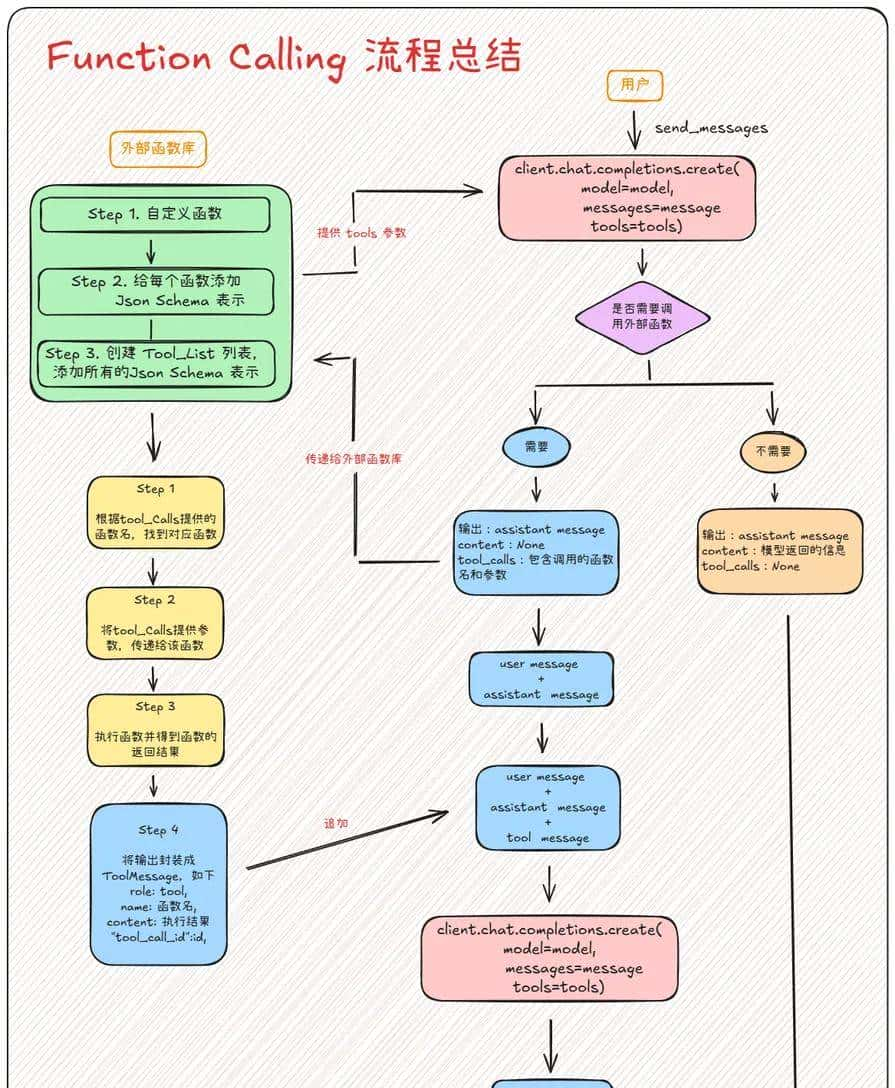
- 定义外部函数与工具描述
import json
import requests
import os
def get_weather(loc):
"""
查询即时天气函数
:param loc: 必要参数,字符串类型,用于表明查询天气的具体城市名称。
注意:中国的城市需要用对应城市的英文名称取代,例如查询北京市天气,loc 输入 'Beijing'。
:return: OpenWeather API 查询即时天气的结果(JSON 字符串)。
:raises Exception: 当网络请求失败或 API Key 错误时可能抛出异常。
"""
api_key = os.getenv("OPENWEATHER_API_KEY") # 请确保已设置此环境变量
url = "https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather"
params = {
"q": loc,
"appid": api_key,
"units": "metric", # 使用摄氏度
"lang": "zh_cn" # 输出语言为简体中文
}
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
return json.dumps(response.json())
# 定义工具描述,供模型理解
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
'name': 'get_weather',
'description': '查询即时天气函数,根据输入的城市名称,查询对应城市的实时天气',
'parameters': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'loc': {
'description': "城市名称(英文),如 'Beijing'",
'type': 'string'
}
},
'required': ['loc']
}
}
}
]2. 执行 Function Calling 完整流程
以下代码展示了如何处理模型返回的工具调用请求,执行函数,并生成最终回答。
def run_function_calling_demo():
"""
演示 DeepSeek Function Calling 完整流程
"""
client = OpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY"), base_url="https://api.deepseek.com")
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "请问北京今天天气如何?"}]
# 第一次调用:模型判断是否需要调用工具
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-reasoner", # 使用 reasoner 模型体验思考过程
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
)
# 获取工具调用信息
tool_calls = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls
if tool_calls:
# 将模型的响应(包含工具调用意图)加入历史消息
messages.append(response.choices[0].message.model_dump())
# 遍历所有工具调用请求
available_functions = {"get_weather": get_weather}
for tool_call in tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# 执行函数
function_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_response = function_to_call(**function_args)
# 将函数执行结果加入历史消息
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"content": function_response,
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
})
# 第二次调用:模型根据函数执行结果生成最终回答
final_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-reasoner",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
)
print("最终回答:", final_response.choices[0].message.content)
if hasattr(final_response.choices[0].message, 'reasoning_content'):
print("思考过程:", final_response.choices[0].message.reasoning_content)
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_function_calling_demo()
四、LangChain 集成与 DeepSeek Reasoner 兼容性解决方案
这里就不过多展开了, LangChain 教程可参考 LangChain 1.0 入门实战教学 只需更换对应API KEY即可。这里主要讲解目前 LangChain 1.1 版本与 DeepSeek-V3.2 Reasoner 推理模型的兼容性解决方案。
LangChain 提供了便捷的 Agent 开发接口,但目前 LangChain 1.1 目前与 DeepSeek-V3.2 Reasoner 模型的兼容性存在必定问题(主要在于推理内容的流式处理和工具调用的解析)。
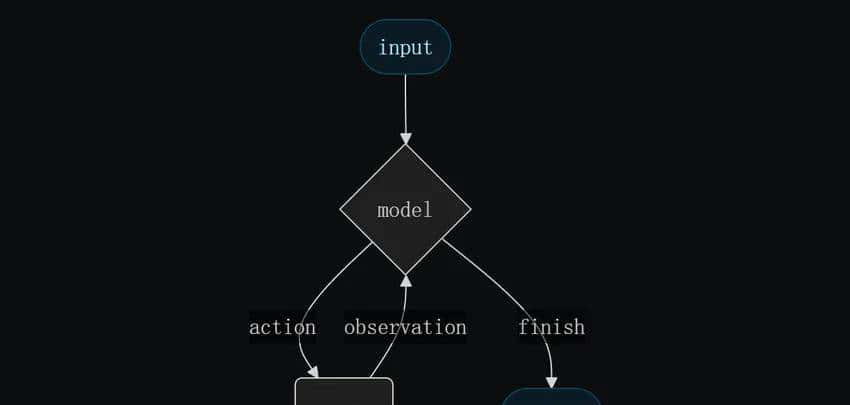
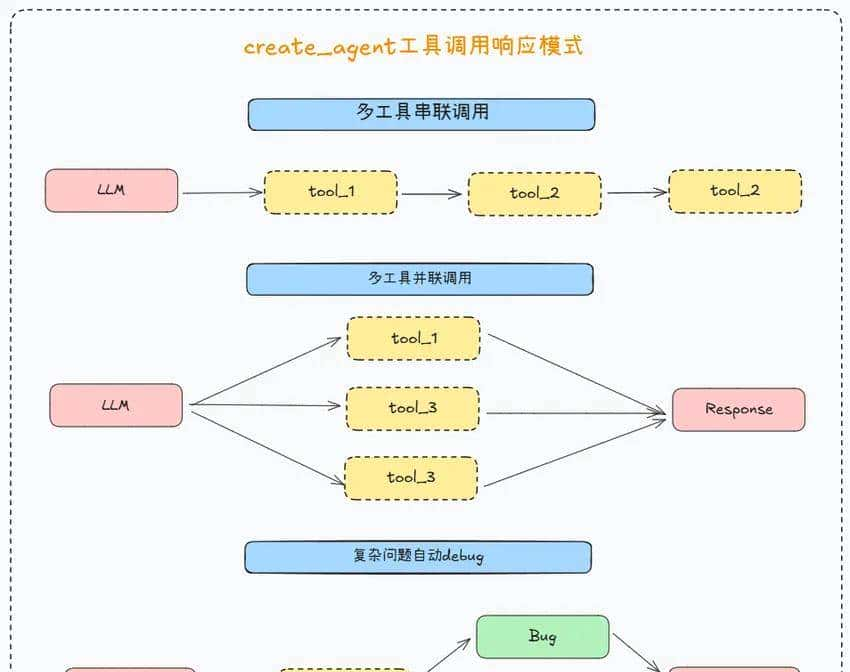
自定义 DeepSeekReasonerChatModel
为了解决兼容性问题,我们通过继承 BaseChatModel 创建自定义模型类,实现以下特性:
- 与 LangChain 的 create_agent 兼容。
- 正确处理 reasoning_content 字段。
- 支持完整的工具调用流程。
from typing import Optional, List, Dict, Any
from langchain_core.language_models.chat_models import BaseChatModel
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, ChatResult, ChatGeneration
from langchain_core.tools import BaseTool
from openai import OpenAI
class DeepSeekReasonerChatModel(BaseChatModel):
"""
自定义 DeepSeek Reasoner 模型类。
该类解决了 LangChain 默认组件无法正确处理 DeepSeek Reasoner 模型
reasoning_content 字段和工具调用的问题。
"""
api_key: str
base_url: str = "https://api.deepseek.com"
model_name: str = "deepseek-reasoner"
temperature: float = 0.7
bound_tools: Optional[List[Dict]] = None
_client: Any = None
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self._client = OpenAI(api_key=self.api_key, base_url=self.base_url)
@property
def _llm_type(self) -> str:
return"deepseek-reasoner"
def _convert_messages_to_openai_format(self, messages):
"""
将 LangChain 消息格式转换为 OpenAI API 格式。
:param messages: LangChain 消息列表
:return: OpenAI 格式的消息列表
"""
openai_messages = []
for msg in messages:
role = "user"
if msg.type == "ai":
role = "assistant"
elif msg.type == "system":
role = "system"
elif msg.type == "tool":
role = "tool"
msg_dict = {
"role": role,
"content": msg.content or"",
}
# 处理 tool_calls
if hasattr(msg, 'tool_calls') and msg.tool_calls:
# 这里需要将 LangChain 的 tool_calls 转换为 OpenAI 格式
# 简化处理,假设已经适配或直接传递
pass
# 【关键】恢复 reasoning_content
if'reasoning_content'in msg.additional_kwargs:
msg_dict["reasoning_content"] = msg.additional_kwargs['reasoning_content']
# 处理 tool_call_id
if hasattr(msg, 'tool_call_id'):
msg_dict['tool_call_id'] = msg.tool_call_id
openai_messages.append(msg_dict)
return openai_messages
def _create_ai_message_from_response(self, response):
"""
将 OpenAI 响应转换为 LangChain AIMessage。
:param response: OpenAI API 响应对象
:return: LangChain AIMessage 对象
"""
message = response.choices[0].message
# 处理 tool_calls
tool_calls = []
if message.tool_calls:
for tc in message.tool_calls:
tool_calls.append({
"name": tc.function.name,
"args": json.loads(tc.function.arguments),
"id": tc.id,
"type": "tool_call"
})
# 【关键】保存 reasoning_content 到 additional_kwargs
additional_kwargs = {}
if hasattr(message, 'reasoning_content'):
additional_kwargs['reasoning_content'] = message.reasoning_content
return AIMessage(
content=message.content or"",
tool_calls=tool_calls,
additional_kwargs=additional_kwargs
)
def bind_tools(self, tools: List[BaseTool], **kwargs):
"""
绑定 LangChain 工具到模型。
:param tools: LangChain 工具列表
:return: 绑定了工具的新模型实例
"""
openai_tools = []
for tool in tools:
openai_tools.append({
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": tool.name,
"description": tool.description,
"parameters": tool.args_schema.model_json_schema()
}
})
return self.__class__(
api_key=self.api_key,
base_url=self.base_url,
model_name=self.model_name,
temperature=self.temperature,
bound_tools=openai_tools,
**kwargs
)
def _generate(self, messages, stop=None, run_manager=None, **kwargs):
"""
核心生成方法,调用 DeepSeek API。
:param messages: 消息列表
:param stop: 停止词(暂未实现)
:return: ChatResult 包含生成结果
"""
# 简单实现,实际生产需完善消息转换逻辑
# 注意:此处仅为核心逻辑演示,完整转换逻辑需处理所有消息类型
openai_messages = []
for m in messages:
if m.type == 'human':
openai_messages.append({"role": "user", "content": m.content})
elif m.type == 'ai':
msg = {"role": "assistant", "content": m.content}
if m.tool_calls:
msg['tool_calls'] = [{
'id': tc['id'],
'type': 'function',
'function': {'name': tc['name'], 'arguments': json.dumps(tc['args'])}
} for tc in m.tool_calls]
openai_messages.append(msg)
elif m.type == 'tool':
openai_messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"content": m.content,
"tool_call_id": m.tool_call_id
})
request_params = {
"model": self.model_name,
"messages": openai_messages,
"temperature": self.temperature,
}
if self.bound_tools:
request_params["tools"] = self.bound_tools
response = self._client.chat.completions.create(**request_params)
ai_message = self._create_ai_message_from_response(response)
return ChatResult(generations=[ChatGeneration(message=ai_message)])使用自定义模型创建 Agent:
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def write_file(content: str) -> str:
"""
将指定内容写入本地文件。
:param content: 需要写入的内容
"""
with open("output.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(content)
return"写入成功"
# 初始化模型
model = DeepSeekReasonerChatModel(
api_key=os.getenv("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY"),
model_name="deepseek-reasoner"
)
# 创建 Agent
tools = [get_weather, write_file]
agent = create_agent(model=model, tools=tools, system_prompt="你是一个有用的助手。")
# 运行 Agent
result = agent.invoke({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "查询北京天气并写入文件"}]})
print(result['messages'][-1].content)五、结语
本篇我们从 0 到 1 走完了使用 DeepSeek-V3.2 模型 Agent 开发的基础路径。欢迎加入 赋范大模型技术社区:
https://brmes.xet.tech/s/4mjiyo 免费领取完整项目教程及源码,我们还有更多Agent开发实战等你来拿。

















暂无评论内容