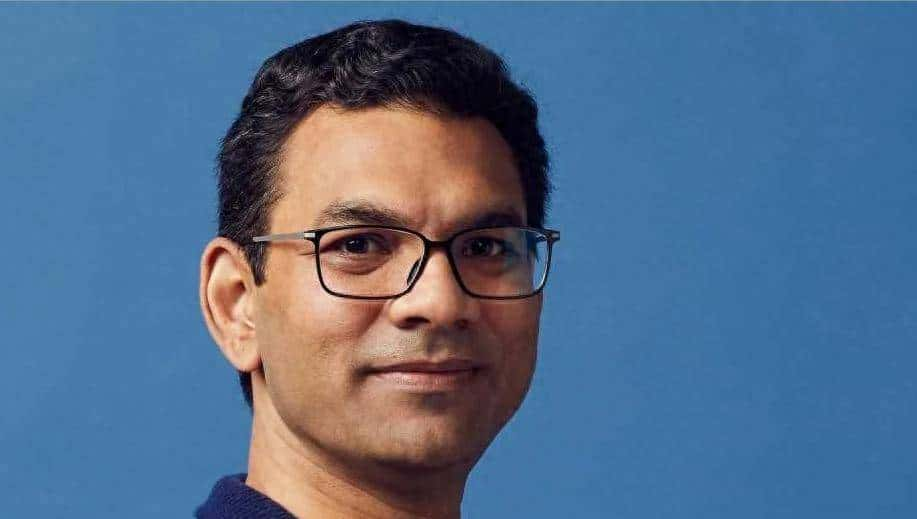

PayPal四分之一个世纪的数字化转型是什么样子的
PayPal目前处理的支付量超过1.3万亿美元,在过去25年中一再声称自己是数字成功的故事。但业内人士一致认为,这种增长需要可靠的技术架构不断支持才能蓬勃发展。
如果有一家公司可以吹嘘自己是100%的数字原生代,那就是PayPal,该平台允许公司和消费者以安全,舒服和有利可图的方式发送和接收数字支付。自 1998 年以来,该品牌随着技术的发展和增长,如今,其网络规模和消费者使用使其成为数字支付系统中家喻户晓的名字。
最初,该公司从 x.com 和Confinity作为一家加密公司出现,开发P2P支付并使用PalmPilot的Beam技术。“随着时间的推移,我们变成了一种基于电子邮件的支付解决方案,所以只要有一个电子邮件地址,你就可以收到钱,”PayPal执行副总裁兼首席技术官Sri Shivananda说。很快,该品牌成为非官方的第三方服务提供商,eBay用户将其作为付款方式包含在商品描述中。“eBay看到了欢迎我们加入他们的机会,最终,我们被收购,成为他们的官方支付服务,”Shivananda补充道。“我们与eBay携手成长,并在2015年分离后继续这样做。
自PayPal成立以来,创新和技术一直是该品牌成功不可或缺的一部分,Shivananda说,该品牌经历了初创阶段,成长阶段,扩张阶段的发展,然后以平台心态定位自己,他说,使用云理念,整合收购,统一数据资产,并使用数据科学和人工智能。
一、一个策略,五个关键
从技术角度来看,该品牌的战略引擎分为五个投资领域。根据Shivananda的说法,安全性是重中之重,由于在安全漏洞不断增加的环境中为客户提供值得信赖的平台至关重大。“当我们谈论安全时,昨天足够的东西今天已经不够了,”他说。“PayPal和许多其他大公司一样,每秒都会遭受攻击,我们只能通过具有增强的安全层和可靠技术的架构(如人工智能)来管理如此多的威胁。
稳定是另一个目标。对于信任PayPal作为其业务支付手段的 35 万商家来说,优质、可靠且始终可用的服务至关重大。“我们有责任确保每笔有效交易都完成并到达商家手中,”他说。
另一个基本部分是速度,即以高于行业的速度保持创新的能力。Shivananda说,为了做到这一点,该公司在其平台、工具和产品开发生命周期流程上投入了大量资金,以改善流程并消除执行过程中出现的障碍。“这使我们能够提高开发人员的生产力和创造力,”他说。
从 2016 年到 2022 年,该公司的支付处理量从 354 亿美元增加到去年的 1.36 万亿美元。Shivananda说,这种增长“需要得到技术架构的支持,这种架构可以通过增加容量来增长,而不需要繁重的工程、重建或重新架构工作。换句话说,可扩展性。
最后是效率。“当我们在这些领域工作时,我们必须密切监控效率和支出,以确保我们的每笔交易成本最低,并确保我们在所有技术领域保持卓越运营。
为了应对这些挑战,PayPal拥有一支高素质的技术团队,去年,全球在技术和开发方面的投资超过3亿美元。Shivananda说:“我们的技术员工队伍在全球范围内和所有地区运营,因此我们从每个人身上学到不同的经验教训,并将其应用于我们运营的其他市场。“这也使我们能够在所有市场拥有最好的全球技术、欺诈缓解和预防以及网络安全措施,同时遵守当地法规和合规要求。”
二、技术层
为了使所有这些战略领域尽可能顺利地流动,PayPal的技术分为四个主要层面。最低层是基础设施,由数据库和数据湖组成。这些应用程序存在于无数服务器上,但有些技术托管在公共云中。这种组合使公司能够连接世界各地的客户,并提供他们期望的速度、价值和可靠性。用户数据也位于此层中,包括配置文件、行为、事务和风险。简而言之,它是PayPal的结构骨架。
第二层由支撑所有PayPal产品和服务的一组技术组成。“我们称它们为基础平台,它们使我们能够有效地使用底层基础设施,”他说。这些平台由一系列功能组成,例如开发人员和工程师的内部工具,或缓存,消息传递,密码管理和密码学等服务,“这对我们的业务至关重大,”他补充道。“这就像PayPal的神经系统。
下一层称为通用平台,是构成产品和服务的技术所在的位置,包括身份(用户身份验证)、支付(交易)、风险(信任和安全)、合规性(履行所有司法管辖区的义务)、隐私(保护上下文信息)、税收、金融(资金流动)和资金(资金管理)。根据希瓦南达的说法,这是PayPal的大脑。
第四个称为商家、消费者和开发人员体验层,其中包括 Web 界面、移动应用程序和 API,允许客户以交互方式和编程方式使用 PayPal 的服务。这被认为是心脏,最接近客户的东西。
三、前瞻性的颠覆性技术
尽管该品牌手中掌握着各种尖端技术,但与业务未来发展最相关的技术之一是人工智能。“我们已经为此工作了十多年,包括基于变压器的深度学习,”Shivananda说。“今天,我们将AI和ML应用于我们的业务,包括减少欺诈,风险管理,客户保护,个性化服务和全球贸易授权。
作为一家拥有超过 431.200 亿活跃账户的公司,它看到了人工智能在创造下一代支付和商业方面的巨大潜力。在两端释放价值的数据是关键。“目前,PayPal拥有超过<>PB的支付数据,具有竞争优势,具有有价值的信息,并有可能为消费者和商家带来更好的商业体验,”他说。
人工智能影响的一个例子可以从2019年到2022年看到,当时该公司的损失率降低了近一半,部分缘由是算法和人工智能技术的进步。“今天,由于我们在人工智能方面的进步,我们可以快速适应不断变化的欺诈模式,以保护我们的客户,”他说。“PayPal的深度学习模型可以在两周内训练并投入生产,对于更简单的算法来说,速度甚至更快。这使我们能够使用最新的生产数据训练模型,纳入新的欺诈模式,并从内部代理和客户那里获得反馈。
该品牌还致力于塑造下一代数字货币和相应的金融基础设施。为此,PayPal投资了自己的技术、人员和专注于区块链的公司,并申请了与加密货币相关的专利。“鉴于我们作为一家值得信赖的数字支付公司的经验以及我们与监管和金融生态系统的牢固关系,我们信任我们的区块链、加密货币和数字货币(BCDC)团队的结合,以及我们在技术和监管基础设施方面的投资,将为我们在这个领域的愿望提供一个坚实的平台。
最终,目标是推动数字资产的包容性、普遍性和实用性,以进一步定义商业和价值交换的未来。
本文来源于CIO.COM,由数智化转型网翻译而成,转载时请备注文章来源及翻译来源。
英文原文:
What a quarter century of digital transformation at PayPal looks like
Currently processing a volume of payments worth over $1.3 trillion, PayPal has repeatedly staked its claim as a digital success story over the last 25 years. But insiders agree this growth needs to be constantly supported by reliable technological architecture in order to thrive.
If there’s a company that can boast being 100% digital native, it’s PayPal, the platform that allows companies and consumers to send and receive digital payments in a secure, comfortable and profitable way. Since 1998, the brand has evolved and grown in step with technology, and today, the size of its network and consumer use has made it a household name in digital payment systems.
Initially, the company emerged from x.com and Confinity as a crypto company, developing P2P payments and using PalmPilot’s Beam technology. “Over time, we became an email-based payment solution, so just by having an email address, you could receive money,” says Sri Shivananda, PayPal EVP and CTO. Soon, the brand became an unofficial third-party service provider that eBay users included as a payment method in item descriptions. “eBay saw the opportunity to welcome us into their fold and, eventually, we were acquired, becoming their official payment service,” Shivananda adds. “We grew hand in hand with eBay and have continued to do so after separating in 2015.”
Since PayPal’s inception, innovation and technology have been integral to the brand’s success, which, says Shivananda, has been developed through the start-up phase, growth phase, expansion phase, and then positioning itself in a platform mentality, he says, using the cloud philosophy, integrating acquisitions, unifying data assets, and using data science and AI.
One strategy, five keys
From a technological point of view, the brand’s strategic engine is divided into five investment areas. According to Shivananda, security is the top priority since it’s essential to offer a trusted platform to customers in a climate of increasing security breaches. “When we talk about security, what was enough yesterday is no longer enough today,” he says. “PayPal, like many other large companies, suffers attacks every second, and we can only manage this volume of threats through an architecture with reinforced security layers and solid technology, such as AI.”
Stability is another objective. For the 35 million merchants who trust PayPal as a means of payment in their businesses, it’s vital the service is high quality, reliable and always available. “It’s our responsibility to ensure that each valid transaction is completed and reaches the merchant,” he says.
Another fundamental piece is speed, that is, the ability to maintain innovation at a rate higher than that of the industry. To do this, says Shivananda, the company invests heavily in its platforms, tools and product development lifecycle processes in order to improve flow and eliminate barriers that occur during execution. “This allows us greater productivity and creativity on the part of developers,” he says.
From 2016 to 2022, the company went from processing a payments volume of $354 billion to $1.36 trillion last year. This growth, says Shivananda, “needs to be supported by a technological architecture that can grow by increasing capacity, and without requiring heavy engineering, reconstruction, or re-architecture work.” In other words, scalability.
Finally, there’s efficiency. “As we work in these areas, we must closely monitor efficiency and spend to ensure our cost per transaction is the lowest, and that we maintain operational excellence in all technological areas.”
To face these challenges, PayPal has a highly qualified tech team, and last year, global investment in technology and development was more than $3.2 billion. “Our technology workforce operates on a global scale and in all regions, so we learn different lessons from each one, which we apply in the rest of the markets where we operate,” says Shivananda. “This also allows us to have the best in terms of global technology, fraud mitigation and prevention, and cybersecurity measures in all markets, all while complying with local regulations and compliance requirements.”
Technological layers
To make all these strategic areas flow as smoothly as possible, PayPal’s technology is organized into four main layers. At the lowest layer is the infrastructure, made up of databases and data lakes. These applications live on innumerable servers, yet some technology is hosted in the public cloud. This combination allows the company to connect customers around the world and deliver the speed, value and reliability they’ve come to expect. User data is also housed in this layer, including profile, behavior, transactions, and risk. So it’s, in short, the structural skeleton of PayPal.
The second layer is made up of a set of technologies that underpin all PayPal products and services. “We call them foundational platforms and they allow us to efficiently use the underlying infrastructure,” he says. These platforms are made up of a series of functionalities, such as internal tools for developers and engineers, or services such as caching, messaging, password management, and cryptography, “It’s vital for our business,” he adds. “It’s like PayPal’s nervous system.”
The next layer, called Common Platforms, is where the technology that makes up the products and services is located, comprised of identity (user authentication), payments (transactions), risk (trust and security), compliance (fulfilment of obligations in all jurisdictions), privacy (protection of contextual information), taxes, finance (money movement), and treasury (money management). This is, according to Shivananda, the brain of PayPal.
The fourth is called the merchant, consumer, and developer experience layer, which includes the web interface, mobile applications, and APIs that allow customers to use PayPal’s service interactively and programmatically. This is considered the heart, the closest thing to customers.
Forward-looking disruptive technologies
Although the brand has various cutting-edge technologies in its hands, one of the most relevant for the future development of the business is AI. “We’ve been working on this for over a decade, including transformer-based deep learning,” says Shivananda. “Today we apply AI and ML across our business, including for fraud reduction, risk management, customer protection, personalized services, and global trade empowerment.”
As a company with over 431 million active accounts, it sees huge potential in AI to create the next generation of payments and commerce. Data that unlocks value at both ends is key. “Currently, PayPal has more than 200 petabytes of payment data, a competitive advantage with valuable information and potential to drive better commerce experiences for consumers and merchants,” he says.
An example of the impact of AI can be seen from 2019 to 2022, when the company’s loss rate reduced by almost half, in part thanks to advances in algorithms and AI technology. “Today, thanks to our advances in AI, we can quickly adapt to changing fraud patterns to protect our customers,” he says. “PayPal’s deep learning models can be trained and put into production in two weeks, and even quicker for simpler algorithms. This allows us to train models using the latest production data, incorporate new fraud patterns, and get feedback from internal agents and customers.”
The brand is also working on shaping the next generation of digital currencies and corresponding financial infrastructure. To do this, PayPal has invested in its own technology, personnel, and companies focused on blockchain, as well as filed patents related to cryptocurrencies. “Given our experience as a trusted digital payments company and our strong relationships with the regulatory and financial ecosystem, we believe the combination of our blockchain, cryptocurrency and digital currency (BCDC) team, and our investments in technical and regulatory infrastructure, will provide a solid platform for our aspirations in this space.”
Ultimately, the goal is to drive the inclusion, ubiquity and utility of digital assets to further define the future of commerce and value exchange.
本文来源于CIO.COM,由数智化转型网翻译而成,转载时请备注文章来源及翻译来源。
CXOUNION社群成员有:东威科技人力资源总监、卓锦股份人力资源总监、振华新材人力资源总监、宏微科技人力资源总监、唯赛勃人力资源总监、格科微人力资源总监、壹石通人力资源总监、普冉股份人力资源总监、博拓生物人力资源总监、容知日新人力资源总监、国光电气人力资源总监、中控技术人力资源总监、
厦钨新能人力资源总监、长远锂科人力资源总监、悦安新材人力资源总监、海天瑞声人力资源总监、科思科技人力资源总监、宏华数科人力资源总监、倍轻松人力资源总监、艾为电子人力资源总监、华纳药厂人力资源总监、瑞可达人力资源总监、天能股份人力资源总监、中芯国际人力资源总监、九号人力资源总监、锦旅人力资源总监、汇丽人力资源总监、伊泰人力资源总监、凯马人力资源总监、凌云人力资源总监、





















暂无评论内容