
千万级商品库查询超时?Redis才是破局关键
2025年双11大促前夕,某电商平台商品搜索接口突然频发超时告警——MySQL数据库在面对”价格区间300-500元+销量排序+好评率>95%”的多条件组合查询时,响应时间从正常的200ms飙升至3秒以上。架构师团队紧急介入后发现,传统数据库索引在多维度筛选场景下几乎失效,大量查询触发全表扫描。最终他们采用Redis重构查询层,通过Hash+Sorted Set组合结构将查询延迟稳定控制在50ms以内。
这不是个例。当业务从单一条件查询演进到多维度筛选(如电商商品、社交动态、日志分析),Redis作为高性能内存数据库,其丰富的数据结构为复杂查询提供了全新可能。但多数开发者仅停留在String类型的KV缓存,80%的Redis性能潜力被闲置。本文将系统拆解Redis多条件查询的底层逻辑与实战方案,帮你彻底摆脱数据库查询瓶颈。
Hash结构:多字段准确匹配的最优解
Redis Hash结构本质上是键值对的集合,适合存储对象类数据。与String类型需要拼接key不同,Hash可以在一个key下存储多个field-value对,这为多条件查询提供了天然优势。
底层存储机制深度解析
Hash在Redis中有两种编码方式:当field数量少且值较小时使用ziplist压缩列表(内存紧凑),超过阈值后转为hashtable哈希表(查询O(1))。通过hset-max-ziplist-entries和hset-max-ziplist-value配置可调整转换阈值。
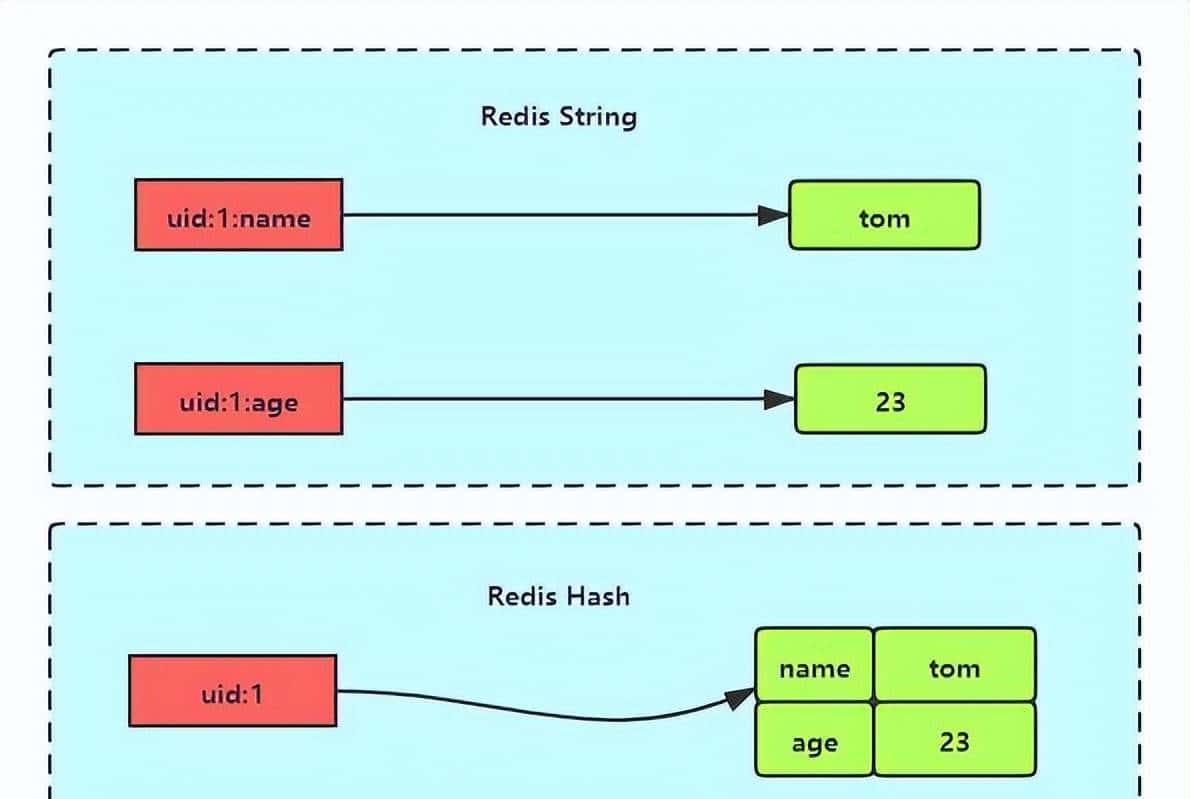
图1:Redis String与Hash存储方式对比,Hash结构可显著减少key数量
实战案例:用户信息多条件查询
假设需要实现”查询用户名为'张三'且年龄26岁的用户”这类多字段准确匹配需求,传统数据库需建立联合索引,而Redis Hash可直接通过field设计实现:
@Service
public class UserHashService {
private static final String HASH_KEY = "user:info";
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
// 存储用户信息,field设计为"username:age"组合
public void saveUser(User user) {
String field = user.getUsername() + ":" + user.getAge();
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(HASH_KEY, field, user);
// 设置过期时间,避免冷数据堆积
redisTemplate.expire(HASH_KEY, 24, TimeUnit.HOURS);
}
// 多条件准确查询
public User queryUser(String username, int age) {
String field = username + ":" + age;
return (User) redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(HASH_KEY, field);
}
// 批量获取所有用户(生产环境慎用,大数据量会阻塞)
public Map<Object, Object> getAllUsers() {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(HASH_KEY);
}
}
HSCAN实现模糊查询
当需要类似SQL的LIKE查询时,HSCAN命令可通过模式匹配实现高效遍历。相比HKEYS命令的全量扫描,HSCAN采用游标分页方式,避免Redis阻塞:
public List<User> searchUsersByPattern(String pattern) {
List<User> result = new ArrayList<>();
ScanOptions options = ScanOptions.scanOptions()
.match(pattern) // 支持*通配符,如"张*:2?"
.count(100) // 每次扫描提议数量(非准确值)
.build();
Cursor<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> cursor = redisTemplate.opsForHash()
.scan(HASH_KEY, options);
while (cursor.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry = cursor.next();
result.add((User) entry.getValue());
}
try {
cursor.close(); // 必须关闭游标释放资源
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("关闭游标异常", e);
}
return result;
}
最佳实践:
- field命名采用”属性1:属性2:…”格式,便于多条件匹配
- 模糊查询优先使用HSCAN而非HKEYS,避免阻塞Redis
- 对超过10万条数据的Hash表,提议按业务维度拆分(如user:info:2025、user:info:2026)
Sorted Set:范围查询与排序的终极方案
当业务需要排序+范围筛选(如”价格>300元的商品按销量排序”),Sorted Set(有序集合)是无可替代的选择。它通过跳跃表(Skip List)实现O(logN)的范围查询性能,远超数据库的B+树索引。
跳跃表如何支撑高效查询?
Sorted Set每个元素包含member和score,内部通过跳跃表维持score有序。跳跃表通过在原始链表上增加多级索引,实现类似”二分查找”的效果。下图展示了查询score介于80-100元素的路径:
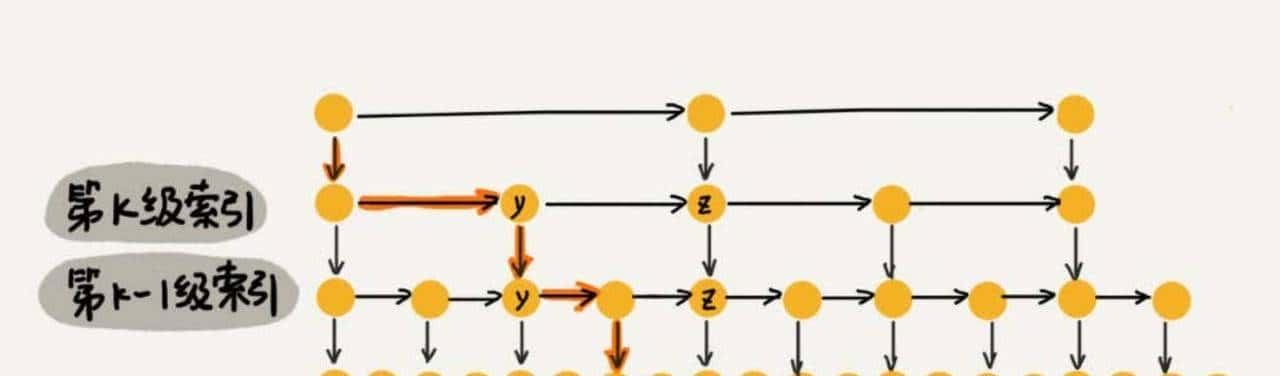
图2:跳跃表明意图,橙色箭头展示查询路径
多条件排序的复合方案
单一Sorted Set只能按一个score排序,实现多维度排序需采用组合键策略:
- 场景:电商商品需支持”价格排序”和”销量排序”
- 方案:创建两个Sorted Set
- goods:price:score=价格,member=商品ID
- goods:sales:score=销量,member=商品ID
- 查询:通过ZRANGEBYSCORE获取符合条件的商品ID,再从Hash表获取详情
@Service
public class GoodsService {
// 添加商品到Sorted Set
public void addGoods(Goods goods) {
// 价格排序集合
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("goods:price", goods.getId(), goods.getPrice());
// 销量排序集合
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("goods:sales", goods.getId(), goods.getSales());
// 商品详情存储在Hash
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("goods:info:" + goods.getId(),
BeanUtil.beanToMap(goods));
}
// 价格区间+销量排序查询
public PageInfo<Goods> queryByPriceRange(double minPrice, double maxPrice,
int page, int size) {
// 1. 获取价格区间内的商品ID(按价格正序)
Set<Object> goodsIds = redisTemplate.opsForZSet()
.rangeByScore("goods:price", minPrice, maxPrice);
// 2. 转换为销量排序(这里简化处理,实际应使用ZINTERSTORE)
List<String> idList = goodsIds.stream()
.map(String::valueOf)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 3. 分页处理
int start = (page - 1) * size;
int end = Math.min(start + size, idList.size());
List<String> pageIds = idList.subList(start, end);
// 4. 批量获取商品详情
List<Goods> goodsList = pageIds.stream()
.map(id -> {
Map<Object, Object> infoMap = redisTemplate.opsForHash()
.entries("goods:info:" + id);
return BeanUtil.mapToBean(infoMap, Goods.class, true);
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 5. 构建分页结果
PageInfo<Goods> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>();
pageInfo.setList(goodsList);
pageInfo.setTotal(goodsIds.size());
return pageInfo;
}
}
ZINTERSTORE实现多条件交集查询
当需要”价格>300元且销量>1000″的交集查询时,可通过ZINTERSTORE命令计算多个Sorted Set的交集:
// 计算交集:价格>300且销量>1000的商品
public Set<Object> intersectGoods() {
// 1. 先获取两个条件的集合
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("temp:price", "goods:price", 300, Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY);
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("temp:sales", "goods:sales", 1000, Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY);
// 2. 计算交集,权重都设为1
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().intersectAndStore(
"temp:price", "temp:sales", "temp:intersect");
// 3. 获取结果并清理临时键
Set<Object> result = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().range("temp:intersect", 0, -1);
redisTemplate.delete("temp:price", "temp:sales", "temp:intersect");
return result;
}
性能提示:Sorted Set的ZRANGEBYSCORE命令支持WITHSCORES参数同时返回分数,ZREVRANGE可实现倒序查询。对于大数据量排序,提议在客户端进行分页而非使用LIMIT,避免Redis内存开销过大。
Bitmap:海量数据的标签筛选神器
当需要处理百万级用户的标签筛选(如”同时满足会员、活跃、地域北京”),Bitmap(位图)以其极致的空间效率成为最佳选择。1亿用户的标签存储仅需12.5MB,远超其他数据结构。
按位运算实现多条件组合
Bitmap将每个用户ID映射为位索引,标签状态用0/1表明。通过BITOP命令可对多个Bitmap执行AND/OR/XOR运算,快速得出多标签交集。
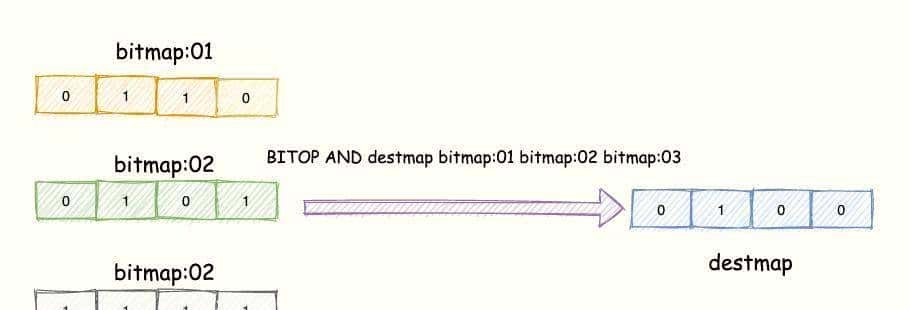
图3:Bitmap按位与运算示意图,实现多标签交集查询
实战:用户画像标签系统
@Service
public class UserTagService {
// 设置用户标签
public void setUserTag(Long userId, String tag) {
String key = "user:tag:" + tag;
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(key, userId, true);
// 设置过期时间(可选)
redisTemplate.expire(key, 30, TimeUnit.DAYS);
}
// 多标签交集查询(同时满足所有标签)
public List<Long> getUsersByTagsAnd(List<String> tags) {
if (tags.size() < 2) {
return getUsersBySingleTag(tags.get(0));
}
// 生成临时键
String tempKey = "temp:bitmap:intersect:" + System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> tagKeys = tags.stream()
.map(tag -> "user:tag:" + tag)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 执行AND运算
redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().bitOp(
BitOperation.AND,
tempKey.getBytes(),
tagKeys.stream().map(String::getBytes).toArray(byte[][]::new)
);
// 查找所有置位的位
List<Long> userIds = findSetBits(tempKey);
redisTemplate.delete(tempKey); // 清理临时键
return userIds;
}
// 查找Bitmap中所有为1的位
private List<Long> findSetBits(String key) {
List<Long> result = new ArrayList<>();
// 使用RedisTemplate.execute执行原生命令
redisTemplate.execute((RedisCallback<Void>) connection -> {
Long offset = 0L;
while (true) {
// BITPOS命令查找下一个置位
Long pos = connection.bitPos(key.getBytes(), true, offset);
if (pos == -1) break; // 没有更多置位
result.add(pos);
offset = pos + 1;
}
return null;
});
return result;
}
}
适用场景:
- 用户标签系统(会员、活跃度、兴趣偏好)
- 签到系统(统计连续签到、月签到天数)
- 在线状态(1亿用户仅需12.5MB)
- 布隆过滤器(去重、判重)
分页优化:从”深分页”陷阱到游标查询
传统LIMIT offset, count分页在offset过大时(如LIMIT 100000, 20)会扫描大量无效数据。Redis提供两种高效分页方案,彻底解决深分页性能问题。
游标分页:大数据集的流式查询
基于SCAN命令的游标分页,通过持续迭代游标获取数据,时间复杂度O(1)。适用于Hash、Set等无序结构:
// 游标分页查询用户
public PageResult<User> scanUsers(String pattern, String cursor, int pageSize) {
ScanOptions options = ScanOptions.scanOptions()
.match(pattern)
.count(pageSize)
.build();
Cursor<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> cursorResult = redisTemplate.opsForHash()
.scan("user:info", cursor.isEmpty() ? "0" : cursor, options);
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
while (cursorResult.hasNext() && users.size() < pageSize) {
Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry = cursorResult.next();
users.add((User) entry.getValue());
}
return new PageResult<>(
users,
cursorResult.getCursorId(), // 下一页游标
cursorResult.hasNext() // 是否有更多数据
);
}
范围分页:Sorted Set的高效分页
基于Sorted Set的ZRANGEBYSCORE或ZRANGE命令,利用score或索引范围实现分页,支持跳页查询:
// Sorted Set范围分页
public PageResult<Goods> zrangePage(String key, double min, double max,
int page, int size) {
long start = (page - 1L) * size;
long end = start + size - 1;
// 获取数据和总条数
Set<Object> goodsIds = redisTemplate.opsForZSet()
.rangeByScore(key, min, max, start, end);
Long total = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().count(key, min, max);
List<Goods> goodsList = convertToGoods(goodsIds); // 转换为商品对象
return new PageResult<>(goodsList, total, page, size);
}
性能对比与选型提议
图4:不同分页方式在100万数据量下的性能对比(单位:ms)
|
分页方式 |
优点 |
缺点 |
适用场景 |
|
LIMIT分页 |
实现简单 |
深分页O(n)性能差 |
数据量<1万 |
|
游标分页 |
O(1)性能,内存友善 |
不能跳页 |
大数据量流式加载 |
|
范围分页 |
支持跳页,性能稳定 |
需要排序键 |
有序数据分页 |
|
Keys扫描 |
全量获取 |
阻塞Redis,O(n) |
禁止生产使用 |
结论:数据量超过1万且需支持跳页时优先使用Sorted Set范围分页;滚动加载场景(如信息流)使用游标分页;严禁在生产环境使用KEYS或HKEYS命令。
Spring Boot集成实战:从配置到缓存一致性
掌握了基础原理,我们通过一个完整案例实现Spring Boot与Redis的深度集成,包含高级配置、自定义序列化和缓存一致性保障。
完整配置方案
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
// 1. 配置Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer序列化Value
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> valueSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance,
ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
valueSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 2. 配置StringRedisSerializer序列化Key
StringRedisSerializer keySerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
// 3. 设置序列化器
template.setKeySerializer(keySerializer);
template.setValueSerializer(valueSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(keySerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(valueSerializer);
// 4. 其他配置
template.setEnableTransactionSupport(true); // 支持事务
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
// 2. 缓存管理器配置
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
// 默认配置
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 默认TTL
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()))
.disableCachingNullValues(); // 不缓存null值
// 特定缓存配置
Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> configMap = new HashMap<>();
configMap.put("hot:goods", config.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(5))); // 热点商品5分钟
configMap.put("user:info", config.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(24))); // 用户信息24小时
return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.withInitialCacheConfigurations(configMap)
.transactionAware() // 事务感知
.build();
}
}
缓存一致性保障策略
分布式环境下,缓存与数据库一致性是必须解决的难题。推荐采用延迟双删+过期时间的组合方案:
@Service
public class CacheConsistencyService {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private GoodsMapper goodsMapper;
// 延迟双删实现
@Transactional
public void updateGoods(Goods goods) {
// 1. 先删除缓存
redisTemplate.delete("goods:info:" + goods.getId());
// 2. 更新数据库
goodsMapper.updateById(goods);
// 3. 延迟500ms后再次删除缓存(解决读写分离场景下的脏数据)
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
redisTemplate.delete("goods:info:" + goods.getId());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
}
// 缓存穿透防护(布隆过滤器)
@Autowired
private BloomFilter<Long> goodsBloomFilter;
public Goods getGoodsById(Long id) {
// 1. 先查布隆过滤器,不存在直接返回
if (!goodsBloomFilter.mightContain(id)) {
return null;
}
// 2. 查询缓存
String key = "goods:info:" + id;
String json = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (json != null) {
return JSON.parseObject(json, Goods.class);
}
// 3. 缓存未命中,查数据库
Goods goods = goodsMapper.selectById(id);
if (goods != null) {
// 4. 写入缓存,设置随机过期时间(防止缓存雪崩)
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSON.toJSONString(goods),
30 + new Random().nextInt(10), TimeUnit.MINUTES);
} else {
// 5. 缓存空值(防止缓存穿透)
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "{}", 5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
return goods;
}
}
缓存注解高级用法
Spring Cache提供了声明式缓存注解,但需注意其局限性:
@Service
public class GoodsCacheService {
// 基础用法:查询缓存
@Cacheable(value = "goods", key = "#id", unless = "#result == null")
public Goods getGoods(Long id) {
return goodsMapper.selectById(id);
}
// 更新缓存:先更新数据库再删缓存
@CacheEvict(value = "goods", key = "#goods.id")
public void updateGoods(Goods goods) {
goodsMapper.updateById(goods);
}
// 条件缓存:只缓存价格>100的商品
@Cacheable(value = "expensive_goods", key = "#id", condition = "#result.price > 100")
public Goods getExpensiveGoods(Long id) {
return goodsMapper.selectById(id);
}
// 注意:@Cacheable不能用在private方法,且类必须被Spring管理
}
避坑指南:
- @Cacheable注解的方法必须是public,且通过Spring代理调用才生效
- 避免缓存频繁变化的数据(如实时库存)
- 缓存键需包含业务标识,防止不同模块键冲突
- 分布式部署时确保所有节点时间同步(影响TTL)
技术选型决策指南与最佳实践
经过前面的深度解析,我们可以清晰看到Redis不同数据结构在多条件查询场景的适用边界。选择错误的数据结构,性能可能相差100倍以上。
数据结构选型决策树
- 是否需要排序?
- 是 → Sorted Set(按score排序)
- 否 → 看字段数量
- 字段数量与查询类型?
- 单字段 → String(简单KV)
- 多字段准确匹配 → Hash
- 多字段标签组合 → Bitmap(AND/OR运算)
- 数据量与性能要求?
- 百万级以下 → 任意结构
- 千万级以上 → Bitmap(空间最优)或Sorted Set(查询最优)
关键结论与最佳实践
加粗重点总结:
- Hash结构适合存储对象数据,多字段准确匹配场景首选,HSCAN命令实现模糊查询需控制count参数避免阻塞
- Sorted Set通过跳跃表实现O(logN)范围查询,是多条件排序+筛选的最佳方案,复合查询需使用ZINTERSTORE
- Bitmap以bit为单位存储,空间效率碾压其他结构,适合百万级用户标签、签到等二值状态场景
- 分页查询必须避免深分页陷阱,Sorted Set范围分页适合跳页场景,游标分页适合流式加载
- 缓存一致性采用”延迟双删+过期时间”方案,结合布隆过滤器防止缓存穿透,随机TTL避免缓存雪崩
进阶学习路径
要真正掌握Redis高级特性,提议按以下路径深入学习:
- 通读Redis官方文档的数据结构和命令参考章节
- 研究Redis源码中跳跃表和压缩列表的实现
- 使用Redis Benchmark测试不同命令在百万级数据量下的性能
- 学习Redis Cluster分布式架构,理解数据分片原理
Redis作为Java开发者必备的中间件技能,其价值远不止缓存。当你能灵活运用Hash、Sorted Set、Bitmap等高级数据结构解决复杂查询问题时,就已经站在了架构能力的新高度。目前就动手改造你的查询系统,让Redis释放真正的性能潜力!
#Java #Redis #中间件 #性能优化 #分布式缓存 #数据结构 #SpringBoot #后端开发
感谢关注【AI码力】,获得更多Java秘籍!



















暂无评论内容