线性回归算法是解决监督式学习中回归问题的重大算法。它是模型假设为线性模型的经验损失最小化算法。在许多实际问题中,对象的特征与其标签之间存在着必定的关系。如果特征与标签之间的关系是近似线性的,就可以用一个线性模型来拟合这种关系。
例子1:简单线性回归
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(1)
# x = -10 + 20 * np.random.rand(30)
x = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, 30)
y = 2 * x + 5 + np.random.normal(0, 0.3, 30)
plt.scatter(x, y)
# 导入sklearn,该包需要先下载安装
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)
model.fit(x.reshape(-1, 1), y)
xfit = np.linspace(-10, 10, 201)
yfit = model.predict(xfit.reshape(-1, 1))
plt.plot(xfit, yfit)
plt.xticks(np.arange(-15, 15, 5))
plt.yticks(np.arange(-30, 30, 5))
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.show()
print(f"直线的系数:{model.coef_[0]:6.2f}")
print(f"直线的截距:{model.intercept_:6.2f}")
运行结果:直线的系数: 1.99
直线的截距: 4.97

上述代码的线性回归结果

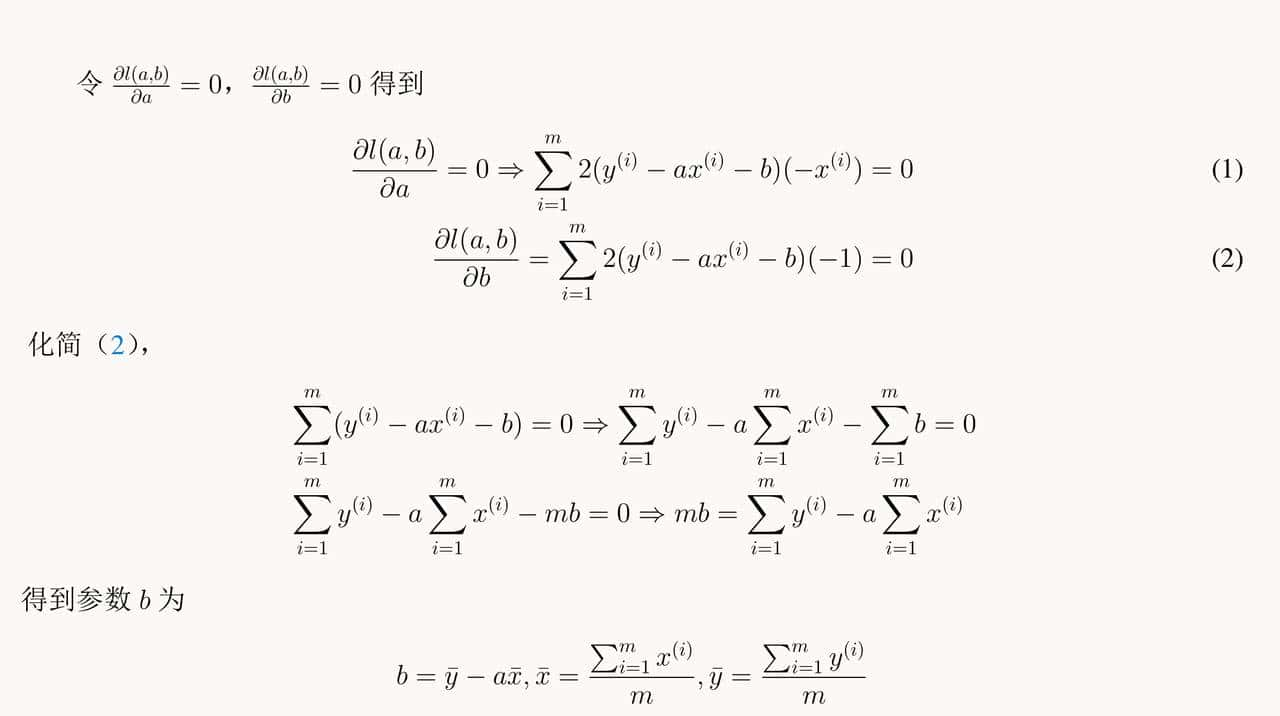
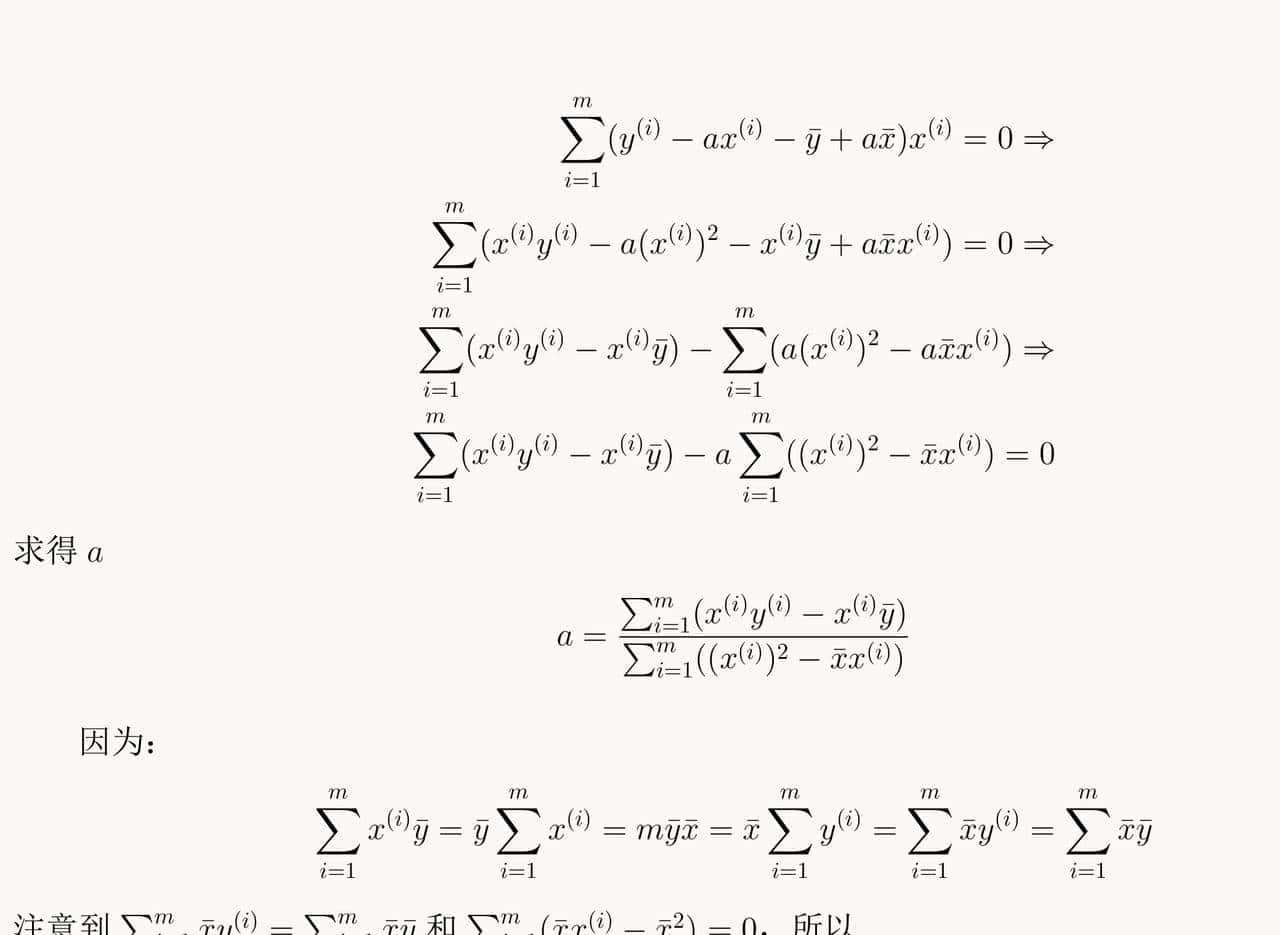
利用上述计算得到的参数,验证其与Sklearn提供的线性回归算法计算的结果的一致性。
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1)
# x = 10 * np.random.rand(10)
# y = 2 * x + 5 + np.random.normal(0, 0.3, 10)
x = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, 30)
y = 2 * x + 5 + np.random.normal(0, 0.3, 30)
x_mean = np.mean(x)
y_mean = np.mean(y)
num = 0.0
d = 0.0
for x_i, y_i in zip(x, y):
num += (x_i - x_mean) * (y_i - y_mean)
d += (x_i - x_mean) ** 2
a = num / d
b = y_mean - a * x_mean
print(f"a={a:6.2f}")
print(f"b={b:6.2f}")
运行结果:
a= 1.99
b= 4.97
斜率和截距与sklearn的结果是一致的。
(注:头条的公式编辑器实在太差了,latex公式要先转换为图片,速度超级慢,直接截图了。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。如内容涉嫌侵权,请在本页底部进入<联系我们>进行举报投诉!
THE END



![在苹果iPhone手机上编写ios越狱插件deb[超简单] - 鹿快](https://img.lukuai.com/blogimg/20251123/23f740f048644a198a64e73eeaa43e60.jpg)
















暂无评论内容